Vigamox Ophthalmic Eye Drops are used to treat bacterial infections in the eye. It should not be use
Vigamox Ophthalmic Eye Drops are used to treat bacterial infections in the eye. It should not be used for fungal or viral infections. Moxifloxacin was first patented in the United States, in 1991 by Bayer A.G., and then again in 1997. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration then approved the drug, Avelox for use in 1999. Moxifloxacin is also produced by Alcon, as Vigamox.
Vigamox composes of the following active and inactive ingredients:
Active: Moxifloxacin (0.5%), Inactives: Boric Acid, Sodium Chloride, and purified water. It also consists of hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide to adjust pH to 6.8.
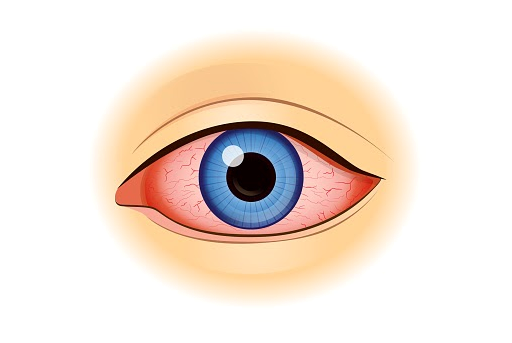
Eye infections can be uncomfortable, painful, and, if left untreated, potentially harmful to your vision. They can affect various parts of the eye, including the eyelids, conjunctiva (the clear layer covering the white part of the eye), cornea, and even the inside of the eye.
Before we discuss whether to see an optometrist or a doctor, let's first identify the symptoms that may indicate an eye infection:
1. Redness: Bloodshot or pinkish eyes are often a telltale sign of an eye infection.
2. Discharge: If you notice a discharge from your eye, whether it's watery, yellow, green, or even bloody, it could be a sign of an infection.
3. Itching or Burning: Persistent itching or a burning sensation in your eyes can signal an underlying issue.
4. Blurry Vision: Any sudden change in your vision, especially if it's accompanied by discomfort, is cause for concern.
5. Sensitivity to Light: Increased sensitivity to light, known as photophobia, is another potential symptom.
6. Foreign Body Sensation: If it feels like there's something foreign in your eye, it may be due to an infection or irritation.
Now that we've identified the symptoms, let's explore whether an optometrist or a doctor is the right professional to consult.
Optometrists are eye care professionals who specialize in diagnosing and treating a wide range of eye conditions, including infections. Here's why you might consider seeing an optometrist for your eye infection:
1. Expertise in Eye Health: Optometrists are highly trained in the field of optometry and have extensive knowledge of eye health and conditions.
2. Convenient Access: Optometrists are often readily available and can provide swift attention to your eye infection.
3. Prescription Medications: They can prescribe medications, including antibiotics and eye drops, to treat your infection.
4. Routine Eye Exams: Regular visits to an optometrist can help detect eye infections early during routine eye exams.
Doctors, particularly ophthalmologists or general practitioners, can also diagnose and treat eye infections. Here are some scenarios where consulting a doctor might be appropriate:
1. Severe Infections: If your eye infection is severe or accompanied by other health issues, a doctor's expertise may be necessary.
2. Underlying Medical Conditions: If you have underlying medical conditions that could complicate your eye infection, consulting a doctor is advisable.
3. Surgical Intervention: In cases requiring surgical treatment or more complex procedures, doctors are well-equipped to provide the necessary care.
Now that you know whom to consult, let's discuss prosthetic eye infection treatment, a topic that is often overlooked but essential for those with prosthetic eyes.
Prosthetic eyes, also known as ocular prostheses, are artificial eyes used to replace natural eyes that have been lost due to injury or disease. Just like natural eyes, prosthetic eyes can also be vulnerable to infections. Here's what you need to know about prosthetic eye infection treatment:
1. Early Detection: Regular check-ups with an optometrist or doctor are crucial to detect infections early in prosthetic eyes.
2. Proper Cleaning: Maintaining good hygiene and cleaning your prosthetic eye as recommended by your eye care professional can prevent infections.
3. Antibiotics: In case of an infection, your optometrist or doctor may prescribe antibiotics or antimicrobial drops specifically designed for prosthetic eyes.
4. Consultation: Always consult your eye care specialist at the first sign of discomfort or redness in your prosthetic eye.
5. Replacement: In severe cases, the prosthetic eye may need replacement to prevent further complications.
Vigamox Eye Drops, scientifically known as Moxifloxacin Ophthalmic, are a prescription medication primarily used to treat and prevent eye infections. These drops belong to a class of antibiotics known as fluoroquinolones and are specifically designed for ophthalmic use.
When it comes to eye infections, rapid and effective treatment is crucial. Vigamox Eye Drops work by inhibiting the growth of bacteria on the eye's surface. The active ingredient, moxifloxacin, targets and eliminates the bacteria responsible for the infection. This action helps alleviate discomfort and promotes the healing process.
Vigamox Eye Drops are typically prescribed by ophthalmologists for various eye conditions, including:
1. Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye): This common eye infection can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or allergies. Vigamox Eye Drops are effective in treating bacterial conjunctivitis, which often presents with redness, itching, and discharge.
2. Corneal Ulcers: These are open sores on the cornea, usually caused by bacterial infections. Vigamox Eye Drops can help in the treatment of corneal ulcers, preventing further complications.
3. Preventative Measures: In some cases, ophthalmologists may prescribe Vigamox Eye Drops as a preventive measure following eye surgery. This helps reduce the risk of post-operative infections.
Proper administration of Vigamox Eye Drops is essential for effective treatment. Follow these steps carefully:
Step 1: Wash Your Hands Before touching your eyes or the eye drop bottle, thoroughly wash your hands with soap and water. This prevents the introduction of additional contaminants.
Step 2: Shake the Bottle Shake the Vigamox Eye Drops bottle gently to ensure that the medication is well-mixed.
Step 3: Tilt Your Head Back Tilt your head backward and look upward.
Step 4: Pull Down Your Lower Eyelid With one hand, gently pull down your lower eyelid to create a small pocket for the eye drops.
Step 5: Administer the Drops Hold the eye drop bottle above the eye and squeeze one drop into the pocket created by pulling down your lower eyelid. Avoid touching your eyes or eyelashes with the dropper.
Step 6: Close Your Eye Close your eye gently and keep it closed for a minute. This allows the medication to be absorbed properly.
Step 7: Repeat if Necessary If you need to administer drops to both eyes or if your doctor has prescribed more than one drop, repeat the process for the other eye.
Step 8: Recap the Bottle After use, securely recap the Vigamox Eye Drops bottle.
While Vigamox Eye Drops are generally well-tolerated, like any medication, they may cause side effects in some individuals. Common side effects may include:
These side effects are usually temporary and mild. However, if you experience severe discomfort or any unusual symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately.
It's essential to follow your ophthalmologist's instructions carefully when using Vigamox Eye Drops. Here are some additional precautions to keep in mind:
Vigamox Eye Drops, containing moxifloxacin, are specifically formulated for the treatment of eye infections in humans. They are not intended for use in treating ear infections. If you suspect you have an ear infection, it is crucial to consult a healthcare professional, such as an ear specialist or an otolaryngologist.
They will be able to properly diagnose the condition and recommend appropriate treatment, which may include ear drops or oral antibiotics specifically designed for ear infections. Using Vigamox Eye Drops in the ear without proper medical guidance is not recommended and may not effectively treat the underlying ear infection.
Vigamox Eye Drops are intended for use in humans and should not be used for dogs or other animals. If your dog has an eye infection or any eye-related concerns, it is important to seek veterinary care. A veterinarian can diagnose the issue and recommend the most suitable treatment, which may include specialized eye drops or medications specifically formulated for dogs. Using human medications like Vigamox Eye Drops on dogs can be unsafe and ineffective, and it should be avoided.
If you are seeking an alternative to Vigamox Eye Drops, it is essential to consult with a healthcare provider or eye specialist who can assess your specific eye condition. The choice of a substitute will depend on the type and severity of the eye infection or condition.
Potential substitutes for Vigamox Eye Drops may include:
1. Azopt Eye Drops: Azopt (brinzolamide) Eye Drops are prescribed for reducing intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension. It is not an antibiotic and is used for different purposes than Vigamox Eye Drops. Azopt works by decreasing the production of aqueous humor in the eye.
2. Azelast Eye Drops: Azelast Eye Drops contain azelastine and are primarily used to relieve itching and redness in the eyes caused by allergies, such as hay fever or allergic conjunctivitis. Azelastine is an antihistamine, and it does not treat bacterial infections like Vigamox does.
3. Careprost Eye Drops: Careprost (bimatoprost) Eye Drops are used to treat a condition known as hypotrichosis, which results in inadequate eyelash growth. These drops are not a substitute for Vigamox Eye Drops, as they serve an entirely different purpose.
4. Cyclomune - 0.1% (3 ml): Cyclomune (cyclosporine) Eye Drops are used to treat chronic dry eye disease by increasing the production of tears. They are not a substitute for Vigamox Eye Drops, as they do not have antibacterial properties.
5. Ciplox Eye Drop: Ciplox Eye Drops contain ciprofloxacin, an antibiotic used to treat bacterial eye infections. Ciplox can be considered a closer substitute for Vigamox Eye Drops when dealing with bacterial eye infections. However, it's essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate antibiotic for your specific infection.
However, only a healthcare professional can determine the most suitable substitute based on your individual needs and medical history.
Vigamox Eye Drops are sometimes prescribed after cataract surgery as a prophylactic measure to prevent eye infections. Cataract surgery is a delicate procedure, and the risk of infection, though relatively low, exists. Vigamox Eye Drops, with their active ingredient moxifloxacin, have antibacterial properties that can help reduce this risk.
Typically, the regimen involves using Vigamox Eye Drops as directed by your ophthalmologist in the days leading up to and following cataract surgery. These drops play a crucial role in maintaining the sterility of the eye during the healing process.
It's essential to follow your ophthalmologist's instructions carefully when using Vigamox Eye Drops after cataract surgery to ensure the best possible outcome and minimize the risk of infection. If you have any questions or concerns about your post-operative eye care, be sure to discuss them with your eye surgeon.
Vigamox Eye Drops can be a valuable tool in treating and preventing eye infections when used correctly. If you have been prescribed this medication, it's crucial to follow your healthcare provider's guidance and report any unusual symptoms promptly.
At V- Carepharmacy, we prioritize your eye health and well-being. If you have any questions or concerns about Vigamox Eye Drops or any other healthcare products, don't hesitate to reach out to us. Your vision is our top priority.
Remember, when it comes to your eye health, knowledge is power. Stay informed, stay vigilant, and prioritize your eye care.
You can purchase Vigamox eye drops from V-carepharmacy's official website or their authorized retail partners.
No, Vigamox eye drops do not have a generic version. It is a brand-name medication.
Vigamox eye drops are priced at $4.50 at V-care pharmacy.
No, you should not use Vigamox eye drops on your dog without consulting a veterinarian. It is meant for human use and may not be safe for pets.
Yes, follow the instructions provided on the medication packaging or by your healthcare provider for the correct dosage and administration of Vigamox eye drops.
The generic name of Vigamox eye drops is Moxifloxacin ophthalmic.
No, you should not use Vigamox eye drops on your dog without consulting a veterinarian. It is meant for human use and may not be safe for pets.
No, you should never use hydrogen peroxide in your eyes. It can be harmful and is not a recommended treatment for eye infections. Consult a healthcare professional for proper treatment.
Eye infections are typically treated by ophthalmologists, who are medical doctors specializing in eye care. They are experts in diagnosing and treating various eye conditions, including infections.
Optometrists primarily focus on vision care and may diagnose eye infections, but they are not medical doctors. If you have an eye infection, it is advisable to seek treatment from an ophthalmologist, who can provide medical treatment and expertise for eye conditions.
Secure, direct ordering: no middlemen, straight from the manufacturer!.
Bin Jarish building,
Deira Dubai, UAE
infovcarepharmacy@gmail.com
+1-614 (887) 8957
DISCLAIMER: This Site Is Not Intended To Provide Diagnosis, Treatment Or Medical Advice. Products, Services, Information And Other Content Provided On This Site, Including Information That May Be Provided On This Site Directly Or By Linking To Third-Party Websites Are Provided For Informational Purposes Only. Please Consult With A Physician Or Other Healthcare Professional Regarding Any Medical Or Health Related Diagnosis Or Treatment Options. The Results From The Products May Vary From Person To Person. Images shown here are for representation only, actual product may differ.
Copyright © v-carepharmacy. All Rights Reserved.